Yes! I'd like to be contacted to schedule a consultation!
You’re a busy general contractor with many responsibilities, from project planning and management to organizing materials and equipment, hiring the right subcontractors, and keeping your build within budget and on schedule.
You don’t always have time to stay current on the technical search engine optimization (SEO) best practices to help your website reach the top of search engine results pages (SERPs).
LinkNow’s search engine optimization specialists have made it easier by putting together the following technical SEO toolbox for you. It’s your blueprint for optimizing your website and positioning your construction business for success.
In this post, we explain why technical SEO is so valuable, walk you through its best practices, and teach you how to follow through with each step.
Table of Contents
Technical SEO is the process of improving your website’s architecture and backend elements to improve its visibility and performance in search engines. It’s a bit like a whole-home remodel in that making strategic site improvements will add considerable value to your online property (your website).
While on-page SEO is about perfecting content and off-page SEO focuses on building community, technical SEO involves paying attention to and optimizing your site’s technical aspects to make it easier for search engines to find, understand, and store your content. This includes backend website optimizations like improving page speed, internal linking, and usability, which help site users and web crawlers better understand and navigate your site.
Search engines like Google value general contracting websites with excellent technical SEO optimization because they provide a better user experience and make it easier for search engine crawlers to understand and index the content on any page. Websites that load quickly, are mobile-friendly, and have clean, organized code are more likely to rank higher in search results.
The higher your general contracting business appears in search results, the more likely local searchers will trust you and click the link to your page.
You want to reach people in your local area searching for a general contracting company. You know your business is the right choice for construction and remodeling improvements, but potential clients won’t choose you until you can climb to the top of search engine results pages (SERPs).
Don’t be intimidated by the process. Just like in the construction industry, the job becomes much easier when you’ve got the technical know-how.
Here’s everything you need to know about technical SEO best practices:
With the increasing use of mobile devices to access information about general contracting services, optimizing your website for mobile viewing is essential. Use responsive design, which adjusts the layout and your site’s content delivery based on the device.
You should test your site on various mobile devices, including tablets, smartphones, laptops, and desktop computers, to see how it looks.
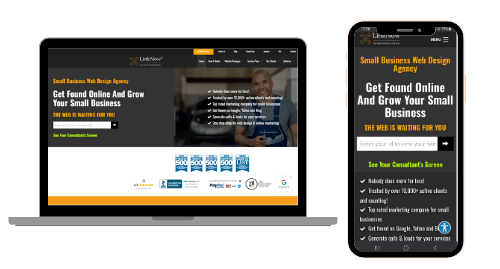
Make sure your website can be viewed on any screen size.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, or HTTPS, is a secure extension of the HTTP protocol used for encrypted communication between web browsers and websites. HTTPS encrypts data transmitted over the internet, safeguarding sensitive information like login credentials and financial details from unauthorized access.

Websites secured with HTTPS will show this in their URL.
Websites using HTTPS have SSL/TLS certificates that verify their identity and encrypt data transmission, ensuring user privacy and security. You should always secure your website with HTTPS encryption to protect user data and improve trust in your company. However, Google also considers HTTPS a ranking factor, so migrating to HTTPS can positively impact your search engine optimization efforts.
Search engines need to crawl and index your website to understand its content. To ensure search engine bots can easily crawl your site:
Developing a simple JavaScript framework for your general contracting web platform will help you deliver an exceptional user experience while ensuring optimal performance and scalability. You can engage visitors and streamline navigation by implementing interactive features and dynamic content, including smooth transitions and interactive forms.
Simplifying your JavaScript code reduces page load times, enhances search engine rankings, and retains visitors. A well-structured framework facilitates scalability and maintainability, enabling seamless expansion and easy code management as your website evolves.
Investing in a simple JavaScript framework lays a solid foundation for a successful and competitive online presence in the general construction industry.
To make each page on your website easy for search engine crawlers to find and index, create an XML sitemap and submit it to each search engine. You should regularly update and maintain your sitemap to reflect changes to your site’s structure and content.
Here’s how to create a sitemap.xml file:
Alternatively, you can use website platforms and content management systems (CMS) that automatically generate and update sitemap.xml files for you. Many CMS platforms, including WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla, offer plugins or modules that can generate sitemaps dynamically based on your website’s content.
Once you’ve created or generated the sitemap.xml file, you can submit it to search engines through their respective webmaster tools (Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools).
Make sure your important pages are indexable by search engines. Avoid blocking important pages with robots.txt directives and use meta robots tags to control indexing behavior on individual pages.
Robots.txt directives are instructions to communicate with web search engine crawlers about how they should crawl and index your website’s content. These directives are typically stored in a text file named “robots.txt” located in your website’s root directory.
Meta robots tags are similar to robots.txt directives in that you can use them to communicate with crawlers. The difference is that where robots.txt directives apply sitewide, meta robots tags are HTML tags used to control how search engines index and display content on specific web pages.
Here are some scenarios when you should use meta robots tags to control indexing:
Use the <meta name="robots" content="noindex"> tag to instruct search engines not to index a specific page. This is useful for pages containing duplicate content, thin content, or pages you don’t want to appear in SERPs.
Use the <meta name="robots" content="nofollow"> tag to instruct search engines not to follow the links on a specific page. This is commonly used for pages that contain links to low-quality or untrusted websites, affiliate links, or pages with user-generated content.
Use the <meta name="robots" content="noarchive"> tag to instruct search engines not to store a cached copy of the page. This is useful for pages containing sensitive information or content you don’t want to be archived by search engines.
Use both the <meta name="robots" content="noindex, nofollow"> tags together to prevent search engines from indexing your page and following the links on it. This is commonly used for pages you want to keep out of search engine indexes and prevent crawlers from following links off your page.
Prevent duplicate content issues by using canonical tags to specify the preferred version of a web page.
Canonical tags, also known as rel="canonical" tags, are HTML elements appearing in the <head> section of your website’s code. You use them to point search engines to the version of a page you want them to see, index, and rank.
Say you have a page about your bathroom remodeling services that users can access from several URLs, like:
You want search engines and users to discover www.generalcontractingexample.com/bathroom-remodeling, so you should add rel=canonical tags to the other two URLs.
They become:
These special tags help search engines understand www.generalcontractingexample.com/bathroom-remodeling should be treated as your page’s primary or canonical version.
Search engines use this information to consolidate indexing signals, attributing all ranking factors (like inbound links and content relevance) to your specified canonical URL.
Canonical tags are handy in the following scenarios:
Schema markup, also known as structured data markup, is a type of code you can add to your web pages to provide search engines with additional information about the content on each page. This markup helps search engines understand what types of information your content provides, leading to more informative and visually appealing search results.
Use structured data markup to give search engines additional context about your content. This enhances search results with rich snippets, including star ratings, event details, and product information.
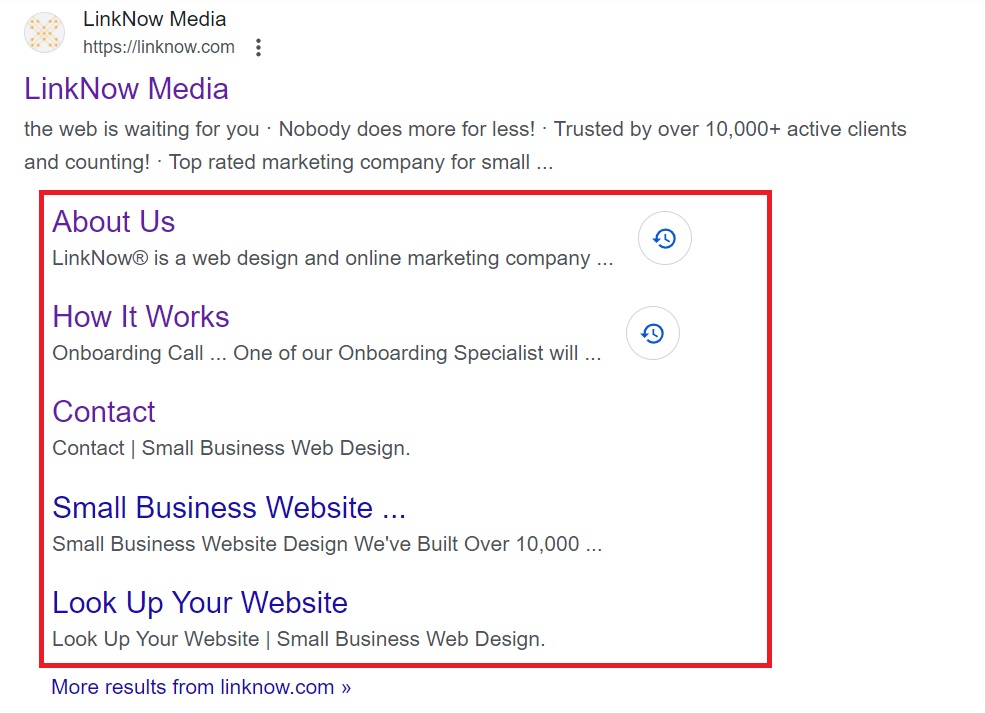
Use structured data markup so search engines pull categories of information from your website and include it on the SERPs.
When you add schema markup to your web pages, you gain the opportunity to provide search engines with specific details about your content, including:
Search engines use schema markup to enhance search results with rich snippets, knowledge panels, and other rich features. These enriched search results improve visibility, click-through rates, and user engagement.
Don’t sleep on schema markup. It’s a powerful SEO technique to help your website stand out from competing general contracting companies in online search results.
Optimize your site’s architecture for users and search engines. Use logical navigation menus, internal linking, and breadcrumb trails to help users and search engines understand the hierarchy of and relationships between your website’s pages.
Flat website architecture is an SEO best practice because it allows users and search engine crawlers to easily access any page on your website with a minimal number of clicks.
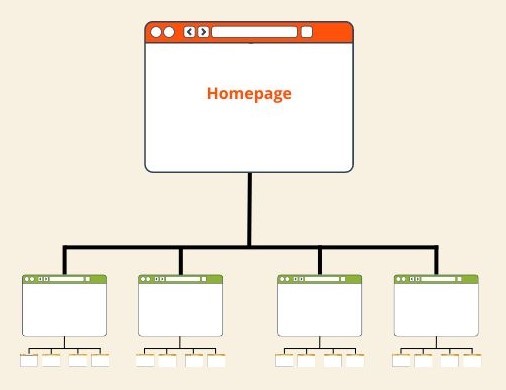
An easily navigated site architecture has pyramid-like layers.
This structure is characterized by a shallow hierarchy, where your homepage links to high-level category pages, which link to sub-category pages, and finally to product or post pages. This pyramid-like structure makes it easy for visitors to reach any page they want in three clicks at most, and it also makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index your content.
Website breadcrumb trails are navigational aids displayed on web pages to show users the hierarchical structure of your website and the path they follow to arrive at the current page. Breadcrumb trails typically appear near the top of your web page and consist of clickable links separated by a delimiter (a greater-than sign or a forward slash).
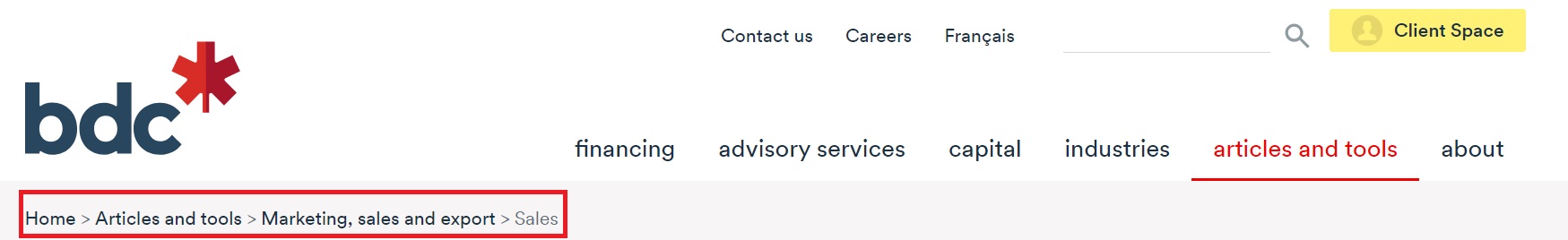
A breadcrumb trail helps users orient themselves on your website.
Breadcrumb trails serve several purposes and can be used effectively in the following ways:
When used effectively, breadcrumb trails are a valuable navigational tool.
Here’s what we recommend:
Creating a logical website navigation menu for a general construction contractor website involves organizing and categorizing your content in a way that’s intuitive for users to navigate and find relevant information.
Follow these steps to create a user-friendly website navigation menu:
Start by identifying the key sections or categories of content that users will expect to find on your website. These go on your main navigation menu.
Common sections for a construction contractor website may include:
Keep your main navigation menu simple and streamlined to avoid overwhelming users with too many options. Limit the number of menu items to 5-7 main sections to achieve clarity and simplicity.
Organize menu items hierarchically, with broader categories at the top level and more specific subcategories nested underneath. For example, “Services” may be a top-level category with subcategories like “Residential Construction,” “Commercial Construction,” and “Remodeling.”
Use clear and descriptive labels for menu items that accurately represent the content within each section. Avoid using vague or ambiguous labels that may confuse users.
Highlight important calls-to-action (CTAs) in your navigation menu, such as “Request a Quote” or “Schedule a Consultation,” to encourage user engagement and conversions.
Think about the typical user journey and how users navigate your website. Ensure your navigation menu facilitates easy access to all relevant content and guides users toward fulfilling their construction goals.
Use internal linking to connect related pages within your website. This helps users navigate your site more easily and distributes link equity throughout your site, improving the visibility of all your pages in search results.
Create descriptive and user-friendly URLs containing relevant keywords that accurately reflect the page’s content. Avoid using dynamic parameters and unnecessary characters in URLs.
Dynamic parameters refer to using query strings or URL variables that follow a question mark (?) in a URL.
Including dynamic parameters in your URLs can have some negative consequences for SEO, including:
Fast-loading websites provide a frustration-free user experience and help your website gain traction in search engine rankings.
To improve loading times, you should:
Minifying CSS and JavaScript files involves removing unnecessary characters, whitespace, and comments from your website’s code to reduce file sizes and improve website loading times.
You can use a minification tool or software to minify the CSS and JavaScript files. Many online tools and standalone software are available for this purpose, including UglifyJS, and online services like Minifier.org for JavaScript and CSS Minifier for CSS.
Consider implementing Gzip compression for your CSS and JavaScript files to reduce file sizes further and improve loading times. Gzip compression is a method of compressing files that minimizes their size and bandwidth.
Browser caching allows web browsers to store images and files locally on a user’s device after they visit your website. This means when the user revisits your site or navigates to another page within your site, their browser can retrieve these resources from the local cache rather than downloading them again from the server—making the process much faster.
There are many online tools available that can compress images without compromising quality. Websites like TinyPNG, JPEG Optimizer, and Compressor.io allow you to upload images and download compressed versions quickly and easily.
Software like Adobe Photoshop also lets you manually adjust image quality and compression settings. You can reduce image file sizes by changing the image dimensions, resolution, and quality settings before saving them for web use.
Be sure to choose the appropriate image format for each image on your website. JPEG is often the best choice for photographs and images with many colors, while PNG is better for images with transparency or text.
Use descriptive file names, alt text, and captions to optimize images for search engines. Compress images to reduce file size without sacrificing quality, which can improve page load times.
Optimize image file names to include relevant keywords users might type into a search engine when looking online for similar images.
Follow these best practices:
Alt text, short for “alternative text,” is a textual description added to an HTML image tag. It briefly describes an image’s content and function for users who may not be able to see it, like those using screen readers.
Alt text should be concise, descriptive, and relevant to the image it describes. It should convey the essential information contained in the image without being too lengthy (125 characters or less).
Don’t add alternative text when an image is purely decorative and doesn’t add meaningful content to your page. Leave the alt text field empty (alt=""). This informs screen readers to ignore the image.
Most internet users have encountered a 404 error when trying to find more information online. It’s that pesky page that comes up to tell you that the link you wanted to visit is no longer working.
You can customize your 404 error pages to provide helpful information and navigation options to users who encounter broken links or missing content. This can reduce bounce rates and keep users engaged with your site.
Along with tracking your SEO statistics, conduct regular audits of your website’s technical SEO aspects using tools like Google Search Console or Semrush. Identify and fix issues, including broken links, crawl errors, and duplicate content, to maintain optimal performance in search results.
You’re a general contractor who knows that quality speaks for itself. Your clients seek your services because they’re confident you’ll work to code and provide the home or commercial new construction or remodeling transformation they desire.
Mastering technical SEO is how you can convey the quality of your business’s web platform to users who find your site. When you use our tips to iron out common SEO problems, your site will climb the search engine results pages toward the coveted number one spot.
Do you wish there was a subcontractor you could hire to take care of technical search engine optimization details for you?
Book a free product demo with our team to learn more about SEO and web design from pros specializing in small business online marketing.